Baker's cyst (popliteal cyst)
A Baker’s cyst is a fluid-filled swelling that can develop behind your knee. It is more common in women and usually develops after the age of 40. Rarely, children and young people with a healthy knee can get a Baker’s cyst.
Causes of a Baker’s cyst
Baker’s cyst is usually caused by a problem in your knee, such as arthritis or a cartilage tear. With these conditions your knee can make too much fluid (synovial fluid), which then collects behind your knee.
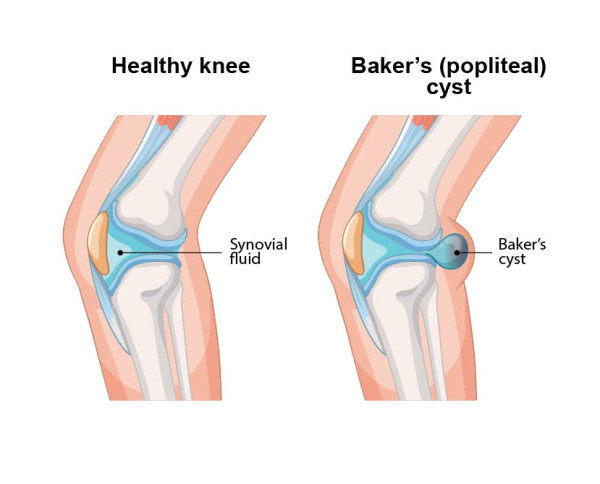
A healthy knee and a knee with a Baker's cyst, or popliteal cyst
Symptoms of a Baker's cyst
Symptoms of a Baker's cyst include:
- tightness or swelling behind your knee
- pain around your knee
- trouble bending your knee.
Rarely, a Baker's cyst can burst causing severe pain, swelling and redness in your calf.
Diagnosing a Baker's cyst
If you have a swollen knee, your healthcare provider may be able to diagnose a Baker's cyst from hearing about your symptoms and examining your knee.
If your healthcare provider wants to rule out another cause for the swelling, you may need an ultrasound or MRI scan of your knee.
If your cyst has burst, you may need tests to rule out deep vein thrombosis (DVT). The symptoms of a Baker's cyst and deep vein thrombosis are the same.
Self care of a Baker's cyst
Simple pain relief such as paracetamol and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen can be useful.
Treating a Baker's cyst
If you have no symptoms or only mild symptoms, you will not need any further treatment. The cyst will usually go away by itself.
If you have ongoing pain or trouble using your knee due to the swelling, there are different options.
- Treating any underlying knee problem. This may include a corticosteroid injection into your knee to reduce inflammation from arthritis. Or it may include surgery to repair cartilage damage.
- Draining the fluid with a needle, sometimes followed by corticosteroid injection into the cyst. The cyst can form again after this treatment.
- Very rarely, surgery is used to remove the Baker’s cyst. This is only considered if the cyst is very large and painful and other treatments have not worked.